-
Changing food consumption patterns has significant potential to help solve pressing challenges related to the food system.
These include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving public health as well as strengthening food security and strategic autonomy. To realise this potential, demand-side food policies – designed to support changes in consumer behaviour – are an essential tool.
-
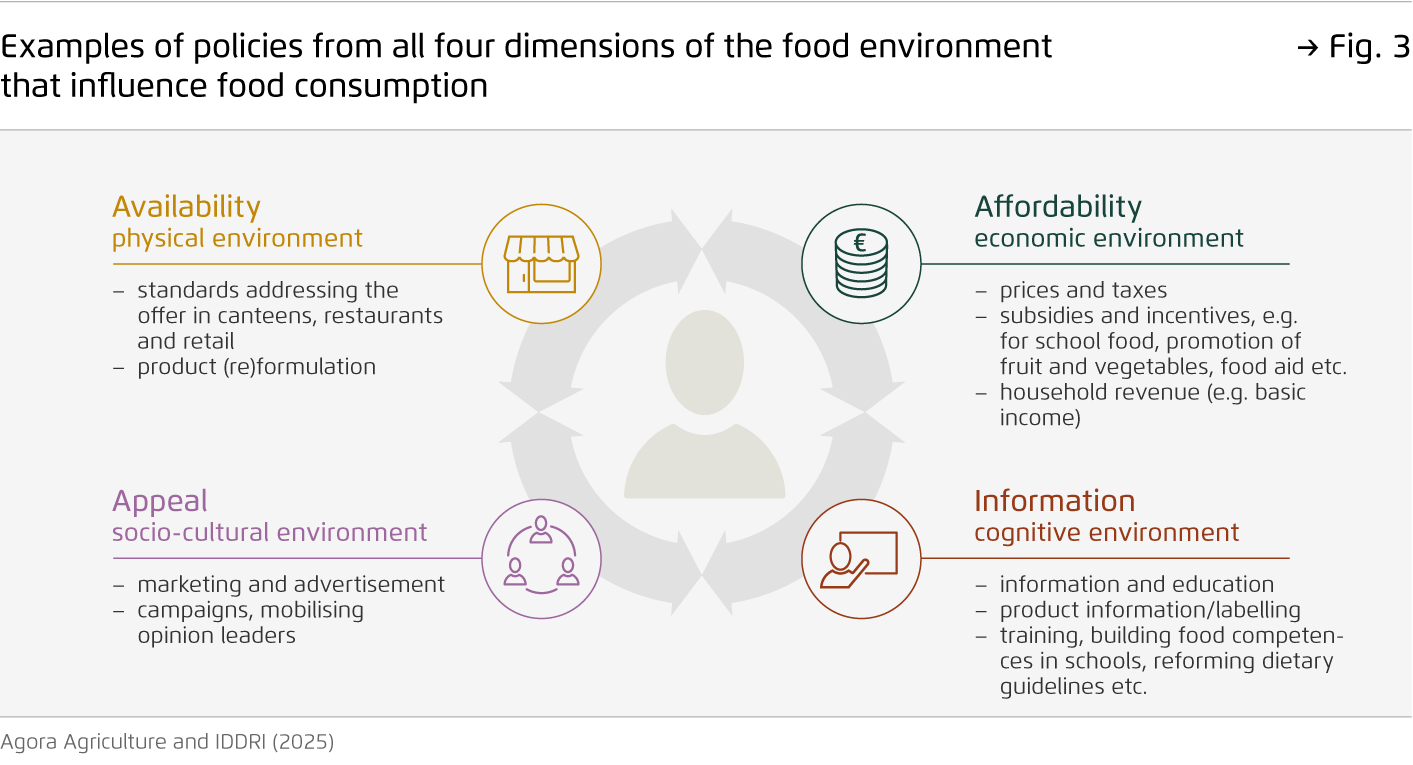
Demand-side policies can help create fair food environments by improving food-related competences and the availability, affordability, and appeal of healthy, sustainable options.
This moves the focus from individual responsibility towards shaping the conditions in which choices are made. It marks a paradigm shift from current policy approaches that mostly focus on consumer education and information – but have limited impact without parallel changes to the broader food environment.
-
Promising examples of demand-side policies are emerging across Europe, offering inspiration for EU Member States.
These initiatives address the different aspects of food environments to make healthy and sustainable options the easy choice. Important policy instruments include public food procurement and product reformulation, labelling and information, marketing and advertising rules and fiscal measures such as taxes and other incentives.
-
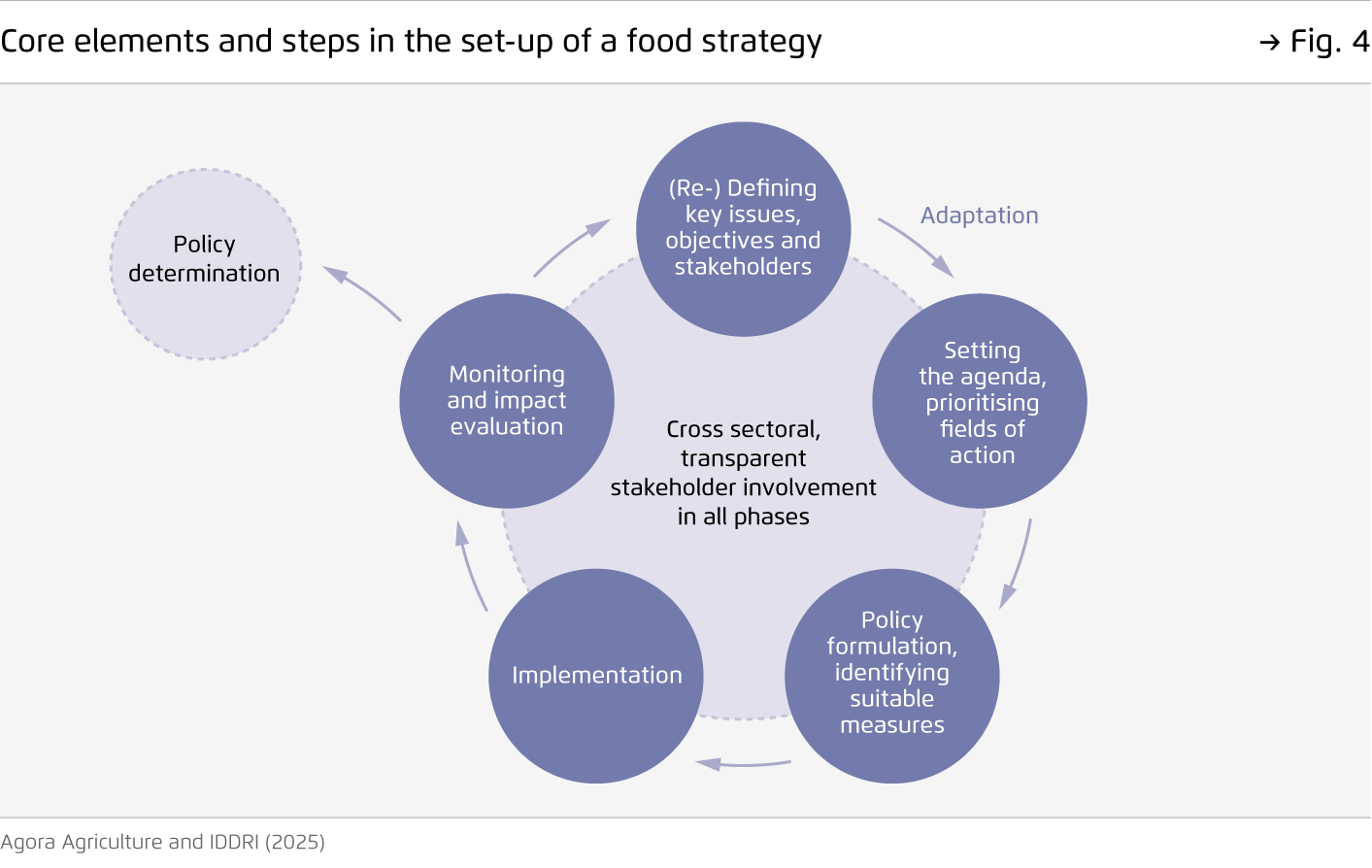
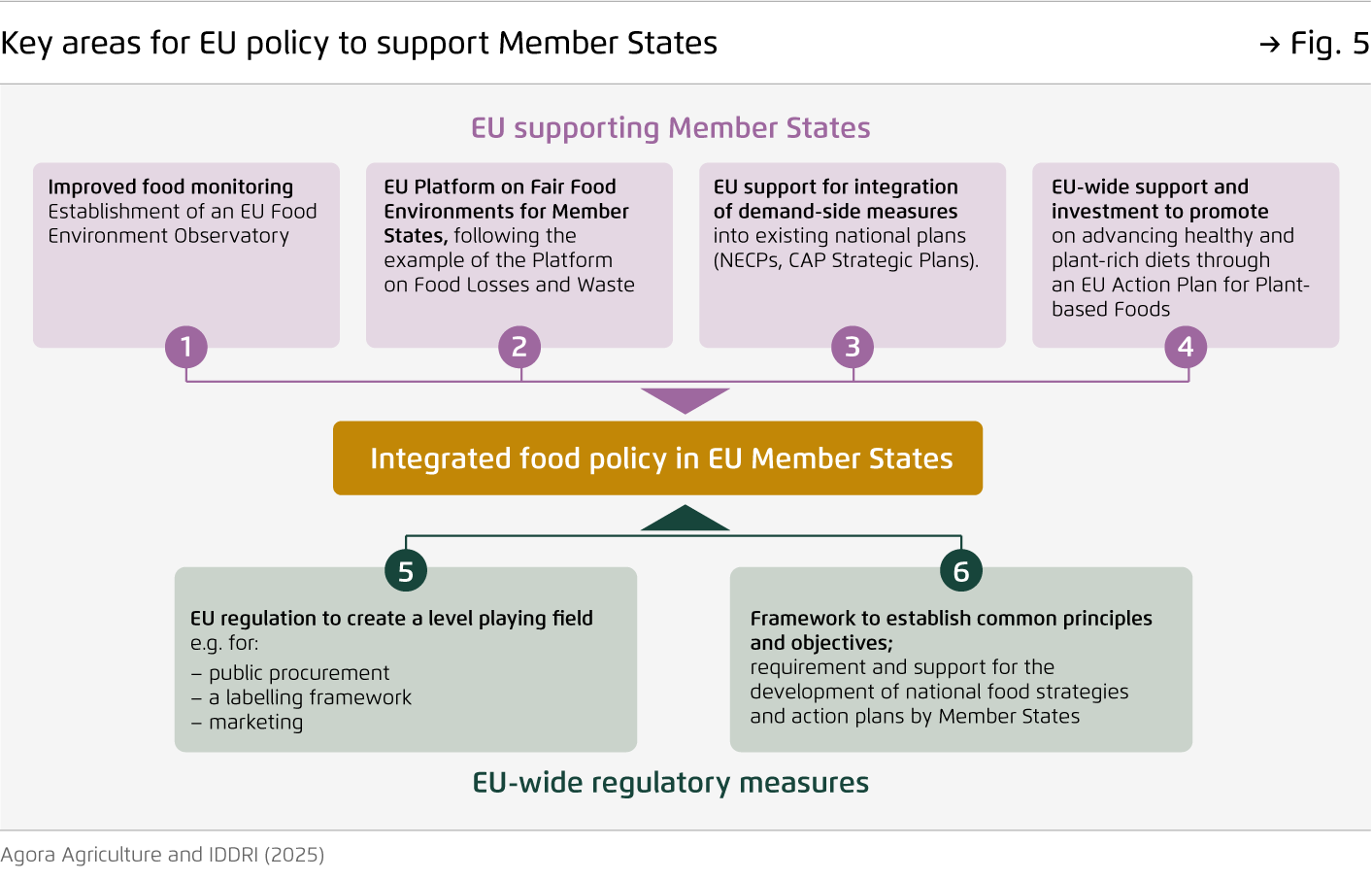
National food strategies and supportive EU-level frameworks can help governments to advance effective demand-side food policies.
Interventions addressing food consumption are often seen as complex and politically sensitive. In this context, an EU platform could facilitate the sharing of best practices and success factors among Member States. At the same time, the development of national food strategies offers a space for negotiation on a shared vision and measures.
Towards food policies that support healthy and sustainable consumption
Country case studies and the role of EU food policy

Preface
Food policy is relevant for a complex set of interconnected challenges, including food security, public health and environmental sustainability. To address these issues effectively, demand-side policies, that support healthy and sustainable consumption patterns are needed. This implies not only new measures, but also a more coordinated approach, one that aligns different policy areas and enhances coherence across local, national and EU levels. Such a coordinated, integrated approach to food policy is still rare among European countries.
With this policy paper, we particularly aim to inform national policymakers in the Member States and at EU level about the potential of demand-side food policies. Specifically, we examined key policies to support fair food environments and thereby improve competence in healthy and sustainable diets as well as their affordability, availability and appeal.
Beyond specific policy measures, we also highlight success factors in the policy development process and examine the potential role of food strategies at the national level. Our insights are illustrated with positive examples from eleven European case studies, which are presented here and detailed in the accompanying report [link]. We conclude with an overview of entry points through which EU policy can best support national food policies.
We hope that this policy paper will be a valuable contribution to the discussion on integrated food policies and their role in building a sustainable, healthy and equitable food system across Europe.
Key findings
Bibliographical data
Downloads
-
Impulse
pdf 2 MB
Towards food policies that support healthy and sustainable consumption
Country case studies and the role of EU food policy
- Attachment pdf 2 MB Case studies from 11 European countries highlighting good practices for demand-side policies
All figures in this publication
Case study examples of this report that help to build fair food environments
Figure 1 from Towards food policies that support healthy and sustainable consumption on page 7

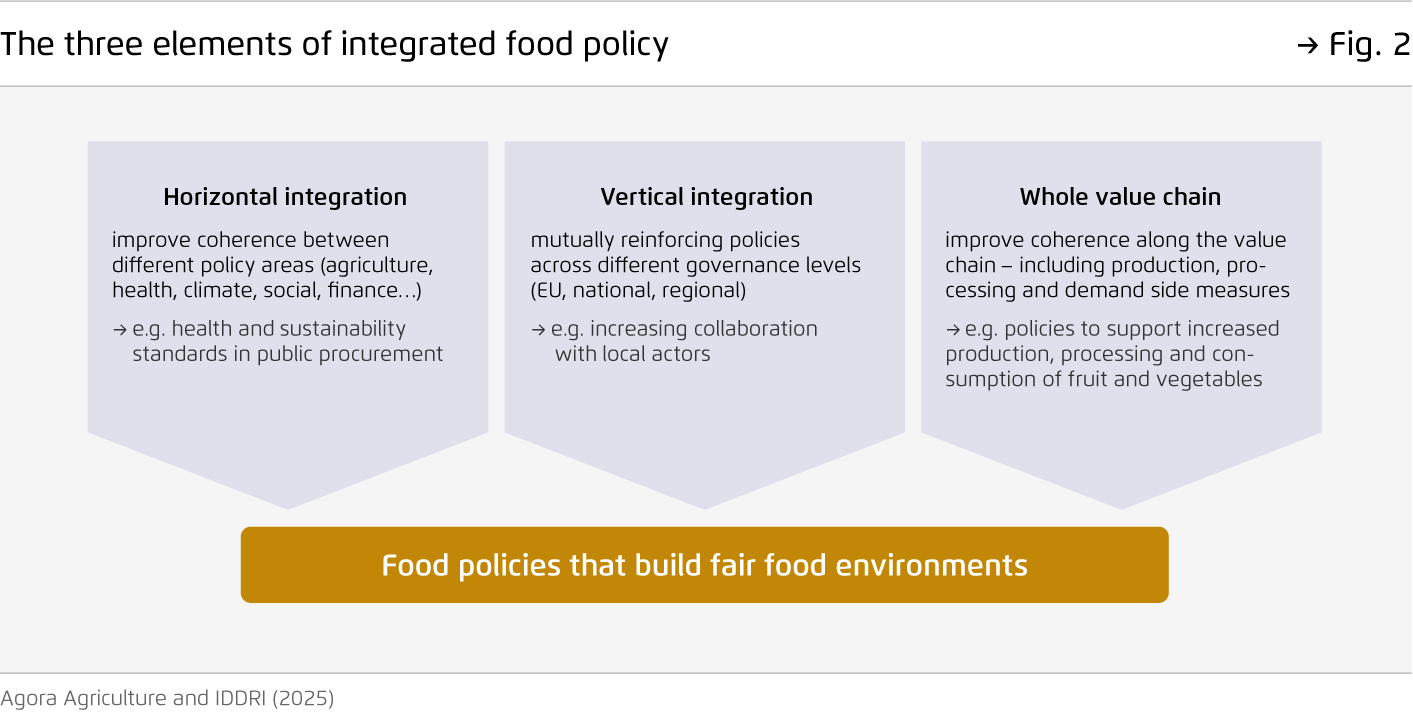
The three elements of integrated food policy
Figure 2 from Towards food policies that support healthy and sustainable consumption on page 13